The power of the law of requisite variety for achieving the client's aimed flow change.
Client: System Engineering Sector
Standard: Product Engineering Process in regulated industry
Year: 2021
Involved people: 125
Involved departments: Software Development, embedded Software Development, System Engineering, Product Management, Security, Safety, Quality, Mechanics, Electronics, Housing, Regulatory, Portfolio Management, Requirements Engineering, Product Marketing, Validation, Production
Our recommended solution was the Socioeconomic Kanban System, aimed at empowering the development flow and establishing focus groups. Additionally, we introduced Ashby’s law of requisite variety, a concept from cybernetics. In simple terms, cybernetics involves understanding how systems operate and regulate themselves. When a manager comprehends cybernetics, they gain insights into managing complex systems effectively. This understanding enables them to make better decisions and optimize the organization’s performance by utilizing the system’s self-regulating and adaptive capabilities.
We supported our client by promoting engagement and empowerment through purposeful decision-making and providing a degree of freedom, while stabilizing the interdependent system through the integration of a Socioeconomic Kanban System. Furthermore, there should be room for sensemaking and purposeful degrees of freedom.

Reducing complexity
During the project preparation phase, we explored various options with our customer to facilitate swift changes with minimal disruption to projects already well advanced in the PEP. Our focus was primarily on products within the sphere of development and its associated organizations, including product management and production. We aimed to establish more structured relationships to achieve the so-called PEP milestones within reduced timeframes between the PEP stages, specifically focusing on products in Stage 1 and Stage 2. Our key objective was to reduce the current lead time for product development by 50%.

Problems of our customer
Thanks to the PEP, the company has standardized document-based product development, which involves numerous requirements and tests. These processes have been digitized to facilitate more effective and cost-saving development but did not meet the experts’ and managers’ expectations. It was not successfully established, resulting in a network of complexity. However, it was complicated finding the puzzles that create opportunities for shorter development and adaptation cycles, minimize the transition to production, and optimize vendor management. Furthermore, it was not possible to find room for sense-making and purposeful degrees of freedom, as well as innovation by saving time through the development phase. Opportunities for shorter development and adaptation cycles, minimize the transition to production, and optimize vendor management. Furthermore, it was not possible to find room for sense-making and purposeful degrees of freedom, as well as innovation by saving time thru the development phase.
We therefore had to bring together the entire management team affected by the change in a workshop to simply explain how we would implement the change together and why it was precisely the commitment of the management that generated trust in the hierarchical structures among the experts.
People who are preoccupied with success ask the wrong questions. They ask, „What is the secret of success“, when they should be asking, „What prevents me from learning here and now?“ Diese mindset promotes self-awareness, adaptability, and a willingness to embrace change, which are essential qualities for achieving one’s goal. By shifting their perspective in this way, they can identify and address the factors that prevent them from making progress in the present moment. During this assignment, we realised for the first time through the assessments that the questions asked were often not targeted.
Challenges in Embracing New Ways: Managers often face difficulties in adopting new approaches due to factors such as risk aversion, comfort with the status quo, lack of understanding, organizational culture, resource constraints, lack of support, fear of failure, short-term focus, and resistance to change.
Key Considerations: Successful adoption of new ways requires addressing these challenges by fostering an innovative culture, providing clear communication about benefits, offering support and resources, aligning with short-term objectives, and overcoming resistance through effective leadership.
Leadership Role: Leaders play a crucial role in creating an environment where managers feel empowered to explore and implement new approaches. Encouraging a culture of learning from failures, providing support, and communicating a compelling vision for change are essential leadership actions.
Organizational Impact: Embracing new ways can lead to increased efficiency, competitiveness, and adaptability. Organizations that encourage innovation and empower their managers to explore new approaches are better positioned for long-term success in dynamic and competitive environments.
Our Recommendations:
- Cultivate Innovation: Foster a culture that values and rewards innovation.
- Clear Communication: Ensure clear communication about the benefits and implications of new approaches.
- Resource Allocation: Allocate resources strategically to support the implementation of new ways.
- Leadership Support: Provide leadership support to address resistance, build trust, and encourage experimentation.
- Learning Culture: Promote a culture where failure is viewed as a learning opportunity, encouraging continuous improvement.
After clearing the unknown, we suggested finding the right Adaptation Zones with so-called focus teams. One of the conditions was that top managers were part of these focus teams. We agreed on a specific time frame for this phase of two weeks.
We suggested finding the right Adaptation Zones with so-called Focus Teams. One of the conditions was that top managers are part of these Focus Teams. Understanding these components is crucial for your transformation.We agreed on a maximum time frame for this phase of three weeks.
The Analogy to football
After about a week, we realized that the principle of Adaptation Zones had not been understood. Our internal analysis gave us the idea of using the football analogy for better comprehension. This approach should help us quickly convey an understanding of the Adaptation Zones, inclusivity, and the functional fit in an easily digestible manner. Our primary consideration was that, with four billion football fans, this analogy could lead to a rapid learning effect. A view enlightening examples:
The Counter-attacks Are One Of Possible The Adaption Zones (green fields)
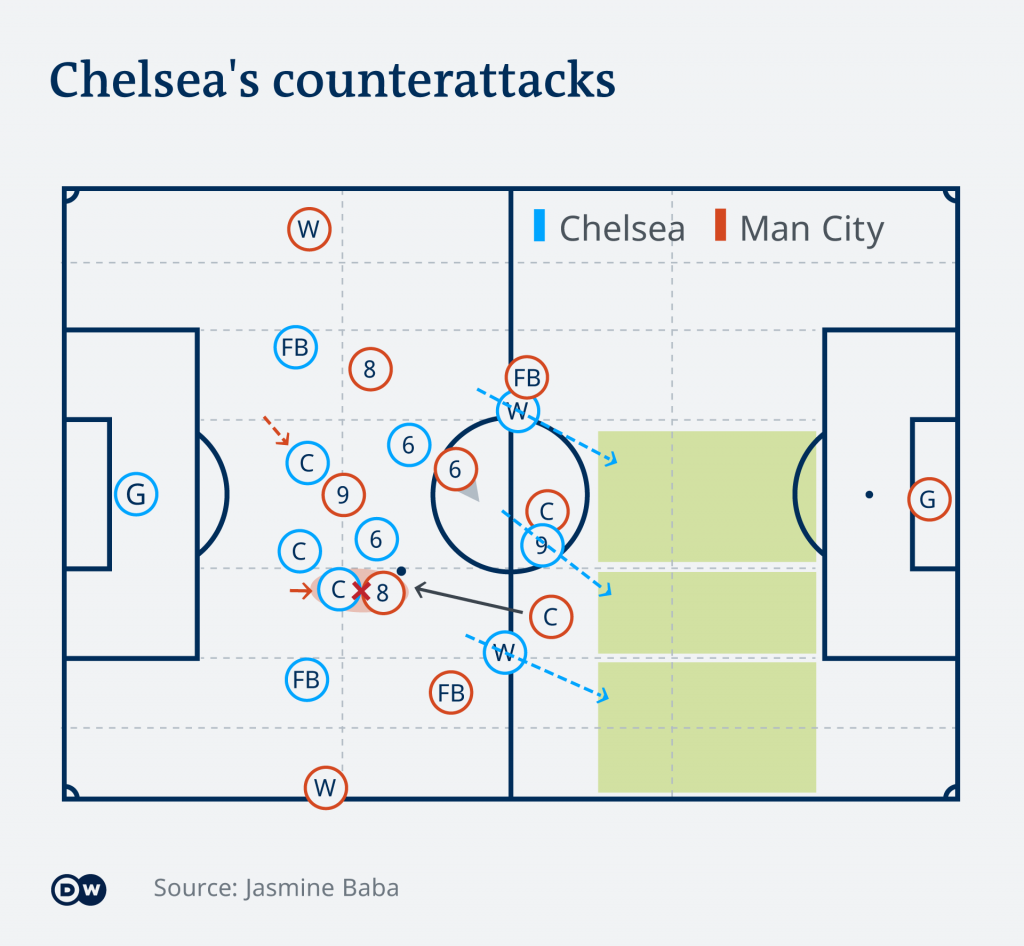
With football schemes, we can extract useful approaches and use the analogies
Dependency Rationalization Zone: Following that, we evaluate the necessity of each subsystem dependency. We identify which dependencies are essential for your system’s proper operation and where streamlining is possible for greater efficiency.
Subsystem Identification Zone:
Kickers in position to find the right and fastest way to the best suitable Adaption Zone at the moment (green field).
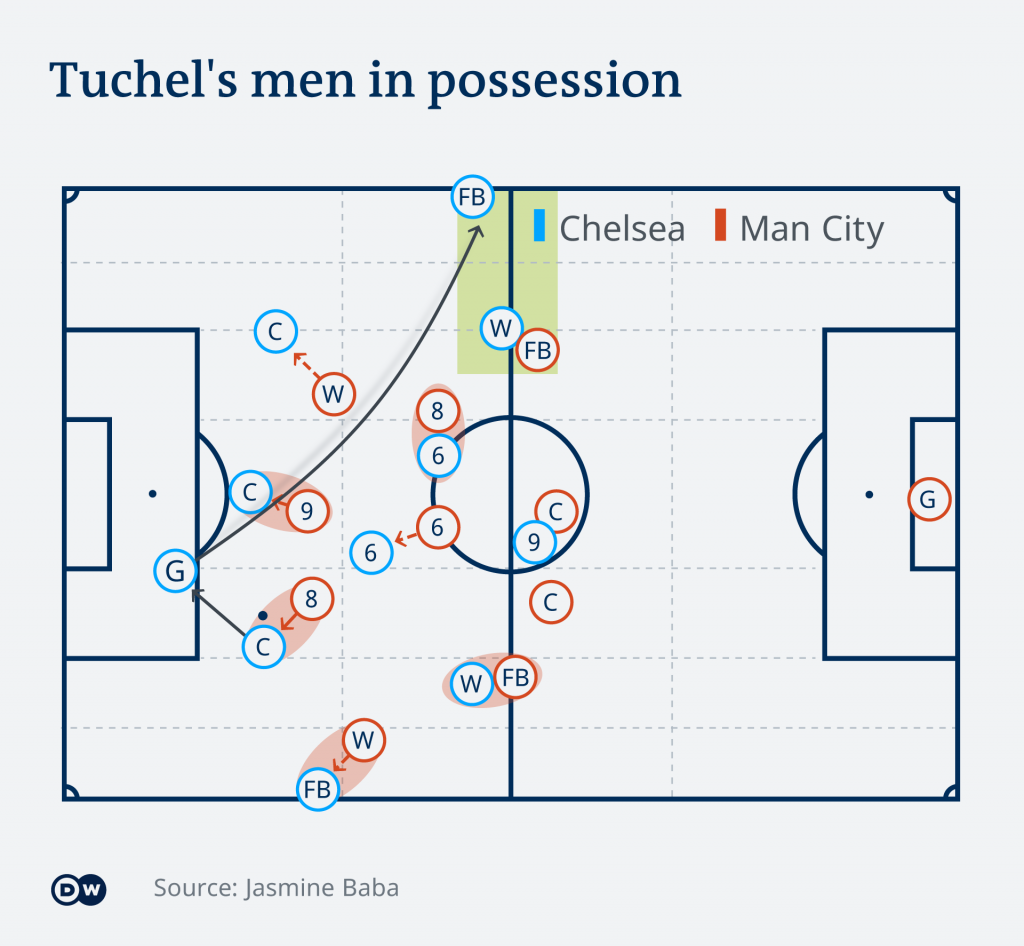
1.Fast changeover of the elasticity and recovery mechanisms
2.Purpose-fulfilling expertise of functional specialists (defender, midfielder, striker, goalkeeper, etc.)
3.The necessity of adaptive systems
4.Economic thinking at all levels (the measure in football is body energy)
5.Adaptive change is permanent work in progress and not static
6.Rapidly incorporating the adaptive change system
7.Fast reduction of transaction costs (ball circulation, line-up)
8.Reducing risk and unpredictability through reliability (played systems)
9.Embracing autopoiesis (Autopoiesis refers to the self-maintaining and self-reproducing systems
10.Adaptive changes are top-down and carried out by the philosophy of the club
Integration Sequence Zone
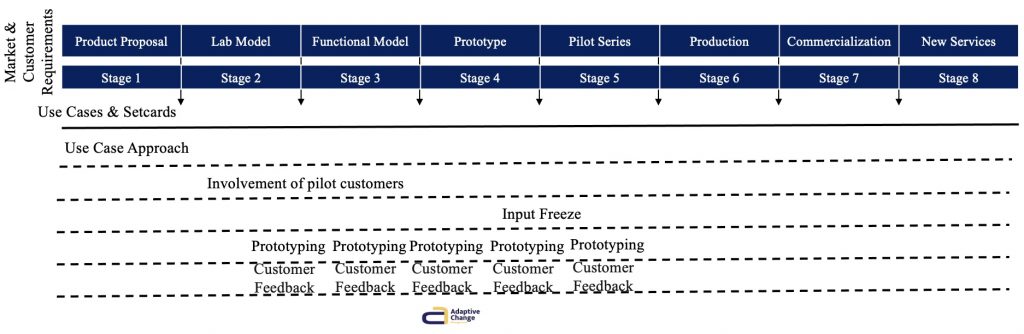
Goals of the change in the PEP
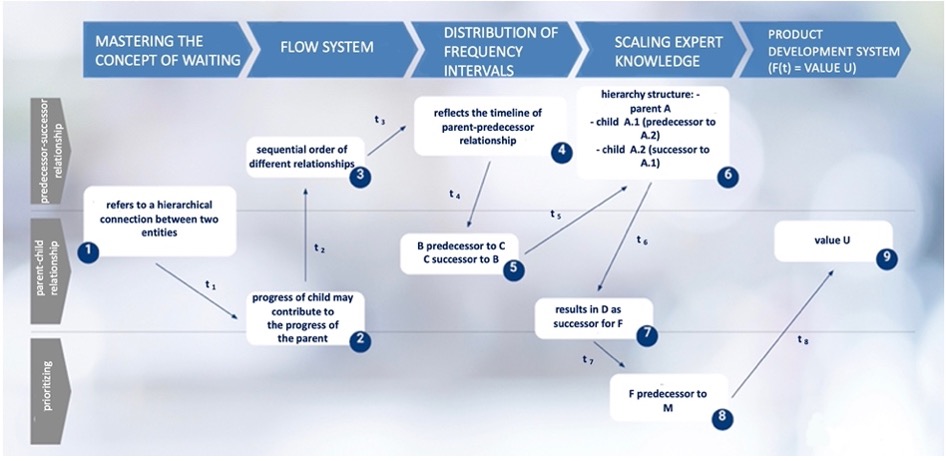
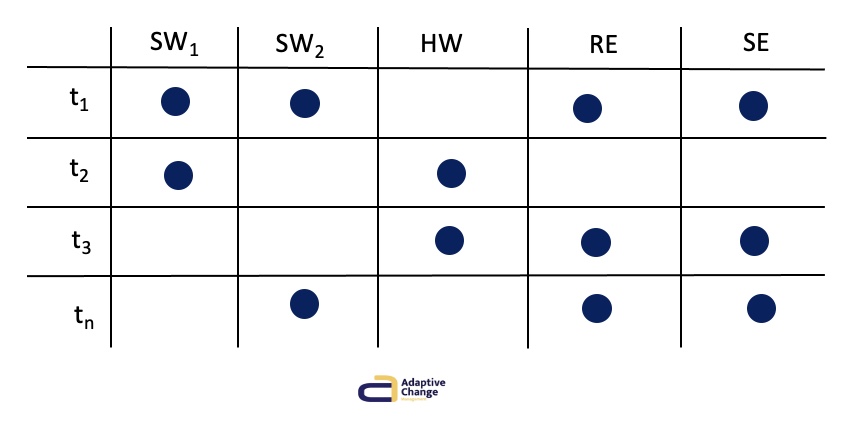
Time Series Analysis Function
SKETCH HOW THE DEPENDENCIES ARE GIVEN
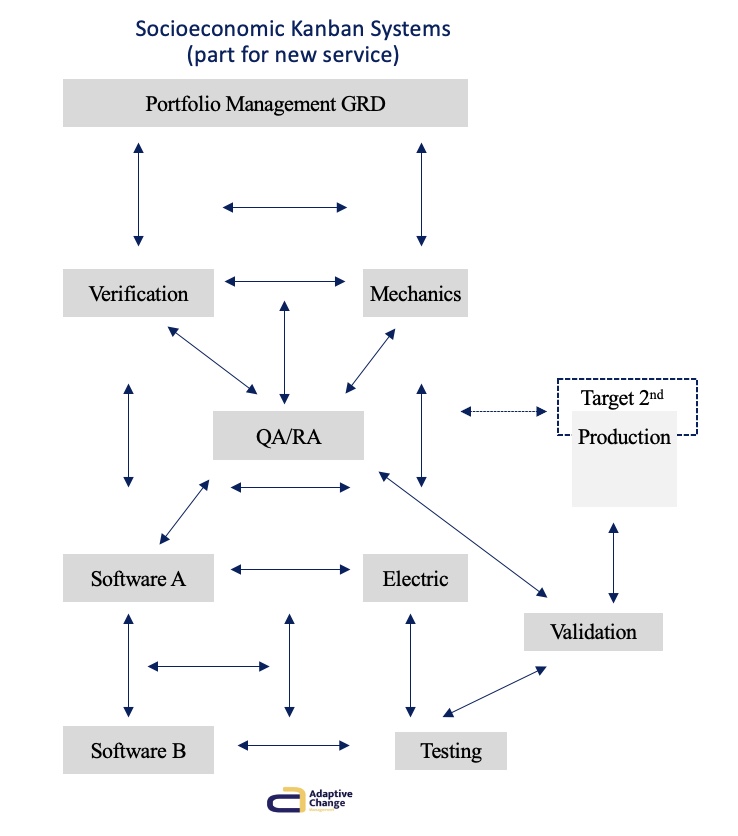
Sociologically the involved departments create social structures in the workplaces that enable them to contribute their full expert functionality combined with digital technology.
We introduced systematic monitoring of variations in ongoing development and incorporated them to re-optimize early on (good regulator).
The very purpose is to rationalize processes to shorten timelines. The second purpose is to determine the value of the requisite variety.
Low costs right from the start
Reducing costs - Step in the Flow
The company has a market-responsive business structure. Functional fit was a major requirement for our client. It refers to how well a product, service, or solution meets the specific functional requirements or needs of the client. It assesses how closely the features and capabilities of a system align with the functional requirements or objectives that are essential for achieving desired outcomes. It’s a measure for the company of how suitable a solution is in terms of its functionality for the intended purpose.
Swifty, measurable outcomes
Increase the speed with prototyping.
Chase friction and remove it systematically,
Ask your People for Value per Change (value for customer, better product, reducing time, etc.).
Daily real-time transparency with digitalization media.
The evidence-based guidance gives managers a new way of understanding of the product development and risk mitigation.
No team first approach
The team first approach as a guiding principle Influenced by the myth that if knowledge-workers are given more control of the processes, they will come up with acceleration, far more better and productive.
Self Power of Company
We experienced with our clients that the self-power of the company for process optimization, organizational change, risk reduction, and goal realization is an unbeatable approach. Decisions made at any level of company contextuality is a valuable social structure (Interdependency).
Permeable Hierachies
Top-down authority for joined-up effort, strategy, worst case scenarios Permeable Hierarchies for trust Individual accountability, rapid initial response Rapid initial response from those closest to problems
Raise Frequency of Prototyping
Every new football match is an adaptation. Every soccer match is a prototype itself. This requires the units that deliver added value for the entire product development process through prototyping.
Time savings with impactful prototypes
Added value for our customer

In the change system of socioeconomic Kanban systems, isn’t it a question of ‘what’ controls should be exercised, but rather ‘how’ controls are implemented in practice with as much purpose as possible? We could support our client in a different way. Waiting and idle time were definitely reduced by 30%. We had gotten rid of the fear of interacting with senior management.
The effects of emergent change on scaling knowledge work
Emergent change: Dealing with challenges that emerge, often have a disruptive character, which for the organisations need to prepare. The change capabilities have an infrastructural character. Adaptive cycle seeks for speedy new combinations.
With more information, transparency, and prototyping, it was possible to include the customer’s in the early stages.
Change to questions based on Monte Carlo Forecasting: prototype, artefact, target date X is ready at Y with a probability of n%.